Description:
- Origin: Mantgomeri district of west Pakistan and ferozpore of Punjab
- Males are commonly used for draft purpose
- Average milk production :1600 liters per lactation
- Fat content :4%
- Average adult body weight: 450-550 kg
Female 200kg
Age of first farrowing:- 283 days
Farrowing interval:- 192 days
Litter size:- 7-8
Gestation period:- 115 days
Body weight:- Male 23kg
Female 35kg
It is a cold freshwater species
Insects remain their dominant food source throughout life, although they are opportunistic piscivores.
The anadromous form of rainbow trout, called the steelhead trout, migrates to the ocean at 1–3 years of age.
Weighing up to 1–3 kg and 3–10 years of age
Average length of the Silver Carp fish is around 60-100 cm.
Silver carp mature at 70 cm TL (5 kg) at an age of 3 to 4 years
The large sized fish can reach as much as 140 cm body length.
It can weight around 50 kg.
This species is known for leaping out of the water when startled (e.g., by noises such as a boat motor).
Breed Purpose |
Dual-purpose (meat, wool) |
||||
| Special Notes | Large animals, very hardy and strong, robust, well known for their docility and good maternal qualities, ewes are excellent mothers, average lambing percentage is between 165 and 180 percent, the ewes produce enough milk for their lambs, although very large in size but they are very easy to keep and manage, good for both meat and wool production, wool is long and broad crimped, meat is of very good quality, lambs grow relatively faster | ||||
| Breed Size | Large | ||||
| Weight | Mature ram’s average live body weight is between 140 and 175 kg, and the mature ewe’s average live body weight vary from 90 to 120 kg. | ||||
| Horns | No | ||||
| Climate Tolerance | Almost all climates | ||||
| Color | White | ||||
| Rarity | Common | ||||
origin: france
large size wool are produced
less prollific breed used for meat purpose as well
Breed Size: Large
Weight: Rams weight between 113 and 135 kg and the ewe’s weight vary from 68 to 90 kg
Horns: Yes
Climate: Tolerance All climates
Color: Can
Very hardy and strong animals, kept for both meat and wool production, well suited to almost all climates, well known for their superior wool and near-mutton breed characteristics
origin: spain
wool production: good
breed type : exotic
distribution: worldwide
popular for good wool production
Small in body /angular in form
Slow maturing
Lambing percentage of 100%
Hardy breed does well under extensive conditions
Have good flocking instincts
They produce fleece that is highly valued
Attains up to 182 cm in length and 38.6 kg in weight
Carnivorous, column feeder
feeds mainly on zooplankton
origin: mexico
weight: 0.9-2.7 kg
height: 15-20 cm
size: small
life span: 12-20 yrs
other characters: loyal, entertaning, good social habit, small and easy to carry, travels well, naturally friendly, more porne to injury, look awesome in clothes, loyal to their own, used in sports as well, require minimum of grooming, they are not tolerate alone condition, intelligence and easy to train, sensetive to cold weather
origin: spain and england
height: 1ft 2 inch - 1ft 3inch
weight: 10-14 kg
life span: 12-15 yrs
size: medium
other characters: very sensetive, benifit from good socilization, gentl, easy to train and handle, very smart, required more attention for their hair, more succeptible for disease than other breed of dog, mostly use for hunting, ear and skin infection is common
The machine is mainly used for land leveling so that moisture is conserved and other operations are also easy to work out. It helps in the reduction in time and water for irrigation, uniform water distribution,lesser weeds in the field, good germination of seeds along with reduction in seed rate, fertilizer requirements.
The machine is used instead of manual weeding for reducing weeding time and overall weeding efficiency. It can be used in every type of crop but the crops should be cultivated in a fixed geometric pattern i.e row to row and plant to plant spacing should be maintained. When used efficiently the machine can remove weed from 2-2.5 ropani land per day.
A disc harrow is a farm implement that is used to till the soil where crops are to be planted. It is also used to chop up unwanted weeds or crop remainders.
Mould Board Plough is the most important plough for primary tillage in canal irrigated or heavy rain areas where too much weeds grow.
The objective forploughing with a Mould Board is to completely invert and pulverize the soil, up-root all weeds, trash and crop residues and bury them under the soil.
The modern combine harvester, or simply combine, is a versatile machine designed to efficiently harvest a variety of grain crops.
The name derives from its combining three separate harvesting operations - reaping, threshing, and winnowing - into a single process.
Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, oats, rye, barley, corn (maize), sorghum, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and canola.
Automatic milking is the milking of dairy animals, especially of dairy cattle, without human labour.
The machine includes teat cups that contact the cow’s teats and remove the milk.
Have vaccum system.
2-3 cattles can be milked at single time.
A brushcutter (also called a brushsaw or clearing saw) is a powered garden or agricultural tool used to trim weeds, small trees, and other foliage not accessible by a lawn mower or rotary mowe
It consists of:
Runs by diesel, petrol and kerosene as well.
Different models of varying pumping capacity are available.
Water pumping capacity of about 25,000 to 1,25,000 litre per hour upto height of 25-32 metre.
A post hole digger is a tool used to dig narrow holes to install posts, such as for fences and signs.
A post hole pincer (pictured) is jabbed into the ground in the open position until the blades are buried. At that point the handles are pulled apart to close the tool and grab the chunk of soil loosened. They are then pulled out of the ground with the chunk of soil. The process is repeated until the hole is deep enough, or until the hole is so deep and narrow that the handles can no longer be pulled apart fully.
Can make holeof 1 metre deep and 2-14 inch wide.
Depending upon the soil conditions can make 45 to 60 holes per hour.
Potential of 1 HP, 26 CC, 4 stroke engine.
Can run for an hour from half litres.
Used in spraying purpose.
Can run by electric power of 0.55 kw.
can spray about 100 m far and spray 420 litre per hour.
A chaff cutter is a mechanical device for cutting straw or hay into small pieces before being mixed together with other forage and fed to horses and cattle.
This aids the animal's digestion and prevents animals from rejecting any part of their food.
Used in spraying purpose.
Features; 1 HP, 26 cc, 2 stroke
Have capacity of about 60 litres.
Can spray 360 litre per hour.
Extensively used in grape vineyards, coffee plantations, orchards, tall-tree, field crops and rubber plantations to ensure pest free field.
A lawn mower (mower) is a machine utilizing one or more revolving blades to cut a grass surface to an even height.
The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the design of the mower, but generally is adjustable by the operator, typically by a single master lever, or by a lever or nut and bolt on each of the machine's wheels
Rotavator is a tractor-drawn implement which is mainly used for seed bed preparation within one or two passes and is suitable in removing & mixing residual of maize, wheat, sugarcane etc., thereby, helps to improve soil health and save fuel, cost, time & energy as well.
It is very useful and effective for puddling (paddy/rice field preparation with water) It’s less weight is strength of the product that allows the rotary tiller to move in loose soil with low HP tractor easily.
The Paddy thresher is to thresh crops. It can be operated by any Tractor & also with 10 HP Electronic Motor. No Paddy is left in the crop & not breakage of Rice in the Paddy. There is a special blower inbuilt for cleaning the Paddy. The capacity of this Thresher is 1 Acre per hour
A hedge trimmer, shrub trimmer, or bush trimmer, is a gardening tool or machine used for trimming (cutting, pruning) hedges or solitary shrubs (bushes). Different designs as well as manual and powered versions of hedge trimmers exist.
A chainsaw is a portable, mechanical saw which cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain that runs along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruning, cutting firebreaks in wildland fire suppression and harvesting of firewood.
Used for sowing different crops such as wheat, barley, maize, peas, black grams, pulses etc. in prepared (tilled) fields with fertilizer.
It can be used to harvest Paddy, Wheat, Maize etc.
It can harvest up to 1.5 m width.
It can harvest 6-7 katha area in 1 hour time period.





Sorghum is popularly known as Camel of crops as it can tolerate exceptional drought. The seeds are high in carbohydrate content with 10% protein and 3.4% fat and contains small amount of minerals and vitamins so have high feeding value.



The succulent, aromatic, and flavorful fruit is eaten fresh, cooked as a starchy vegetable, or preserved (e.g., salted like a pickle).
The nutritious seeds are boiled or roasted and eaten like chestnuts, added to flour for baking, or added as ingredients to cooked dishes.

All parts of an orange, including the seeds and leaves, are rich in vitamin C, which is a powerful antioxidant.
Compounds found in orange peels helps lower cholesterol naturally. Fiber in oranges helps prevent atherosclerosis and protects against rheumatoid arthritis.

Papayas produce an enzyme, papain, which aids digestion and is used to tenderize meat.
Papain has been used in medicine to treat ulcers and reduce skin adhesions following surgery, and studies have shown that it has antimicrobial properties
. Papain is also used to clarify beer, prepare wool and silk for dyeing, and remove hair from hides before tanning, among other uses.
Papaya is usuallydioecious but hermophrodite type and gynodioecious types are also recognized. In dioecious
type, both male and female plants are separate.

Mangoes have recalcitrant seeds which do not survive freezing and drying.
Mango trees grow readily from seeds, with germination success highest when seeds are obtained from mature fruits.
During processing of mango, by-products such as peel and kernel are generated. Kernels take up about 17-22% of the fruit.

The fruits are a rich source of sugar (6-20%), protein 0.7% abd faurkt rucg ub fat (0.3%), mineralslike calcium (10mg) phosphorus (35mg) and vitamins like vitamin C (64mg), vitamin B1 (0..2mg), B2 (0.03 mg and B3 (0.1 mg) per 100g.
The fruits can be canned, made into squash,pickles, and wine or dried to form litchi nut.

Apple seeds are known for containing small amounts of cyanide, a poison without an antidote that makes the blood unable to carry oxygen, resulting in asphyxiation. However, the amount of cyanide in each seed is so small that there is little danger of accidentally consuming a lethal dose.
Apple seeds are coated with a tough, protective layer, keeping them from being digested unless ground or chewed.
This not only protects us from the cyanide, it also protects the seed. If it is not destroyed by the digestive system of animals, it can then sprout wherever they deposit it in their fertile stool.

i) Pegion pea can reach 0.5-4 m in height.
ii) It is perennial shrub grown for its edible pods and seeds.
iii) Pegion pea is fast growing , hardy , widely adaptable and drought resistant plant.
i) It is short-lived perennial, legume usually grown as an annual plant.
ii) Rice bean seeds and vegetable part are also used for fodder.
iii) It is usually 30-100cm in height , but can grow upto 200cm.
i)The horse gram is normally used to feed horses , though it is commonly used in cooking.
ii) It is prescribed for person suffering from jaundice or water retention and as a part of a weight loss diet.
iii) Horse gram are mainly grown under dry land agriculture.
i) Sunflower is annual herbaceous plant and grown for its seed can reach upto 1-3.5m.
ii) It consists of a hard hull (pericarp) and a kernel , which is the actual seed.
i) It is an annual herbaceous plant grown as a cereal crop in the arid and semi-arid areas in Africa and Asia.
ii) It is small grained , warm weather cereal.
i) Buckwheat is an herbaceous annual plant grown for its seeds.
ii) The plant produces many small white or pink flowers which when pollinated, quickly produce seeds.
i) Rapeseed is an herbaceous annual or biennial member of family Brassicaceae primarily grown for the oil which can be extracted from its seeds.
ii) It is third largest source of vegetable oil in the world.
i) Fennel is hardy, perennial herb with yellow flowers and feathery leaves.
ii) It is highly aromatic and flavourful herb with culinary and medicinal uses.
iii) It grows to height of upto 2 – 5 m, with the hollow stem.
i) Lentil is an edible pulse, is a busy annual plant.
ii) Red lentil is a self-pollinating crop.
iii)Seeds are presence inside pods. Each pod contains two seeds.
i) It is the world’s most traded spice and is one of the most common spices added to cuisines around the world.
ii) It is flowering vine which is usually dried.
i) It is annual shrub which can grow to 7 m in height but usually only reaches 1 – 2 m height.
ii) It is a crop generally cultivated for improving soil quality.
iii) It is used as a green manure crop.
i) Cardamom is called the “Queen of spices”.
ii) Cardamom is a herbaceous, perennial, rhizomatous plant of the ginger family, used as a spice.
iii) The seeds and the oil from the seeds are used to make medicine.
i) Black gram is an erect, fast growing annual , herbaceous legume reaching 30 – 100 cm in height.
ii) It is grown for vegetables as well as for forage and hay.
i) Broad bean are excellent protein source.
ii) Broad bean are member of pea family and are one of the oldest known cultivated plants.
iii) It is a stiffly erect plant 0.5 – 1.8 m tall with stout stems of square cross section.
i) Cumin is annual herbaceous plant, with a slender, glabrous, branched stem and grows upto 30 – 50 cm.
ii) Cumin seeds are dried seeds which is excellent source of iron.
iii) Cumin seeds are used as a spice for its distinctive flavor and aroma.
i) It is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or unripe fruit.
ii) It is valued for its high content of protein and micronutrients such as iron and folic acid .
i) Soyabean is the largest oilseed crop.
ii) It is the annual plant that grows upto 1.5 m tall.
iii) Soyabean seed are extremely high in protein content and are grown successfully in regions with high temperature.
i) Mung bean is an annual vine reaching a height of 0.15-1.25m, alternatively known as the green gram ,maash or moong.
ii) Mung bean can be used as cover crop before or after cereal crops.
iii) Mung bean are rich in protein and starch with a low lipid content and variable but generally low amounts of fibre.
i) Field pea is an annual plant with a lifecycle of one year.
ii) It is cool season crop grown in many parts of the world and use as a vegetable crop.
i) Methi is an annual plant with leaves consisting of three small obovate to oblong leaflets.
ii) It is cultivated worldwide as a semiarid crop.
iii) Trigonella means three edges due to the shape of its flower and foenum-graecum is the latin word for the plant that is mixed with poor quality straws to create fragrance.
i) The chickpea plant is an annual sticky herb till 1.64 feet tall.
ii) It is also called Bengal gram or Garbanzo bean or chana.
iii) Chick pea is one of the worlds most consumed pulses.
i)It is also called cilantro , is an annual herb which all parts are edible.
ii) It is used in cuisines throughout the world.
iii) The plant reaches upto 20 inches tall.
i) It is also called linseed which comes from small, single stemmed annual plant that grow to about 2 ft. (0.6 m) tall with grayish green leaves and sky blue flowers.
ii) It is used for extraction of oil known as linseed oil.
iii) It is rich source of Alpha Linolenic Acid ( ALA).
i) Mustard are herbaceous annual plant grown for their seed which are used as spice.
ii) The lower leaves are deeply lobed , while upper leaves are narrower and not lobed.
iii) Flowers are actinomorphic and stamens are tetradynamous.
i) Sesame is a flowering plant also called benne.
ii) The fruit is a capsule within which there are from 15-20 seeds.
i) It is an annual grass and comes in two varieties , distinguished by number of rows of flowers on its flower spike i.e. 6 and 2 row barley.
ii) It is lighter than wheat .
i) Maize is an annual grass and is a staple food crop grown all over the world.
ii) Maize plant possesses a simple stem of nodes and internodes.
iii) Male inflorescence is called tassel and female inflorescence is called ear.
i) Wheat is one of the oldest and most important of the cereal crops.
ii) The demand of wheat is increasing due to unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten protein which facilitate the production of processed food.
iii) The main part of the wheat grain are barn, endosperm and germ.
Rice, a monocot is most widely consume as a staple food.
Rice can produce ratoon crops for upto 30 years and requires ample water.
Main parts of rice grain are husk , bran, endosperm and germ.
Onion seed constitutes 38% of oil that is responsible for its aromatic flavor. The seeds are used as flavoring agents while cooking.
The seeds need to be toasted to enhance their fragrant tinge.
The seeds are also added in various forms of bread like naan, paratha, chapatti, etc. In few parts of the world, onion seeds are also used to season fish.
Onions grown from seed almost always perform better than those grown from sets.

Carrot seeds are not true seeds in a botanical sense but are dry fruits called 'schizocarps'.
Seeds are highly variable due to cross-pollination and have undergone extensive breeding programs to increase uniformity.
Hybridization, however, has not produced consistent results.
Seed development and vigor are determined by the conditions under which they are formed.

The most commonly eaten portion is the napiform taproot, although the entire plant is edible and the tops can be used as a leaf vegetable.
The seed can also be sprouted and eaten raw in a similar way to mung bean.
The seeds of radishes can be pressed to extract radish seed oil.
Wild radish seeds contain up to 48% oil, and while not suitable for human consumption, this oil is a potential source of biofuel.


Nutritionally, the richest part of the okra plant is the seed.
Although the oil of the okra seed after processing is edible, and the residual meal following oil extraction is significantly rich in protein, the seed is not traditionally used for either oil or protein, but rather for seedling and regeneration purposes.
The seeds of mature okra pods, sometimes used as poultry feed, are also consumed after roasting, and as a coffee substitute.

There are between 300-500 seeds in a watermelon, depending upon the size of course.
Although usually discarded, the seeds are edible and delicious when roasted.
They are also highly nutritious and high in fat as well.
One cup of watermelon seeds has over 600 calories.

Pointed gourd is perennial dioecious grown as vine.
Propagation is by vine cutting and root suckers.
Seed propagation is avoided due to poor germination and inability to determine sex of the plants before flowering(50% plants may be male).

The immature fruit is green with white seeds.
The fruit turns orange when mature and splits open from top down to reveal bright red seeds.
The immature fruits are often cooked and eaten as a vegetable. They are rich in vitamins A and C.
The fruits are used in folk medicine to treat diabetes. Its juice is applied externally to treat skin disorders and its juice is drunk as a cure for arthritis, rheumatism and asthma.

Bottle gourds are also called "calabashes", they are sometimes confused with the hard, hollow fruits of the unrelated calabash tree, whose fruits are also used to make utensils, containers, and musical instruments.
Calabash fruits have a variety of shapes: they can be huge and rounded, small and bottle shaped, or slim and serpentine, and they can grow to be over a metre long.

Luffa, or loofah, is derived from the Arabic name, louff, for Luffa cylindrica, while the specific epithet, acutangula, means “with sharp edges”, referring to the prominent ridges of the fruit.
Edible Plant Parts (Edible Fruits; Edible Leaves; Edible Flowers), Medicinal (The fibres, charred and fresh fruits, seeds, leaves and sap from the stem of Luffa acutangula have uses in medicine and cosmetics.
Ridge gourd is extremely rich in dietary fiber helps in proper functioning of digestive system

Fiber of mature dry fruits is used as a bath sponge.
As tender fruits are easily digestible and appetizing,it is prescribed for those who are suffering from malaria and other seasonal fevers.
For seed production, the fruits are harvested when they get physiologically mature.

Seeds are high in protein, oil, and minerals (they contain 30% protein and 40–50% oil), and are eaten raw, toasted, or pressed to make oil.
C. pepo has numerous traditional medicinal uses: seeds are toasted and eaten to kill intestinal parasites; fruits are used as a diuretic and anti-diabetic; and a preparation of the flowers has been used to treat jaundice, measles, and smallpox.

The seeds are nutrient-rich, with especially high content of protein, dietary fibers and numerous micronutrients.
The word can refer either to the hulled kernel or unhulled whole seed, and most commonly refers to the roasted end products.
The oil of pumpkin seeds, a culinary specialty in and important export commodity of Central Europe, is used in cuisine,as a salad, and cooking oil.

Fully mature fruit with ripe rind colour are harvested. Mature seeds easily separate from the interior.
For seed extraction by hand the fruits are cut in half length wise and the seeds are scrapped into a container where the seeds and juice mixture are allowed to ferment for a day in water.
Seeds are washed in water and dried under sun.
Drying is continued unit seed moisture reaches to about 10%


There are basically three methods of seed extraction: (1) juice and seed extraction, (2) acid extraction which is not recommended, and (3) extraction by fermentation, which is the preferred method.
Fermentation is the preferred method because it is a natural process that is least harmful to the seed and can destroy bacterial canker and other seed-borne diseases.

The seeds are scattered through the fruit, embedded in a firm placenta.
.Many seeds are formed in a single fruit (800-1000 in long brinjal and 1000-1500 in round brinjal.
The harvested fruits are stored for three to four days until they become soft. This allows the seed to mature fully. The top one-third of the fruit is removed since it contains almost no seed. Then seeds are extracted by suitable methods.

-known as queen of bulbous plants.
-sword lily, with its beautiful flower spike
-Inflorescence with variety of colours and number of pretty florets.


-Third most important commercial cut flower after rose and gladiolus.
-can be cultivated through cutting and seed both.

-bulbous perennial plants.
-native flower of Mexico.

-perennial plants of creeping habit.
-poisonous plant due to calcium oxalate.
-Can be propagated through cutting and seed both.

-Propagated by seed and cutting.
-Dwarf to medium height.
-produces white pink colored scented bloom.

-Height varies from 0.5 to 2.5cm.
-flower color may white ,yellow,pink ,orange.scarlet and orange scarlet.
-Propagated by cutting and air layering both.

-Flower are white at the time of openning but gradually turn into pink and reddish.
-Propagated easily by cutting and layering.

-propagated by cutting and layering.
-bushy shrub,
-Grown for ornamental foliage and beautiful form.

-Flower colour can yellow and red both .
--propagated by division of rhizomes
-flower in two flushes-september-December and february -April.

-propagated by leaf cutting.
-Have fleshy foliage and stem.
-Capable of withstanding long hot spells of drought.
-store sufficient moisture in their succulent body parts.

-Tall shrub growing 2-3 m height.
-Flowers are yellow ,orange or white and funnel shaped.
-Blooms throughout the year.
-Used as ornamental hedge.

-Dwarf to medium tree.
-Evergreen nature.
-bright red coloured flowers appeared in march to october.
-Propagated by seed and layering.

A large,woody shrub with axillary spines.
Propagated from cutting and seed.

-Tall and deciduous nature.
-Dark red colour flower.
Blooms in December to february.
-Propagated by seed.

-Also known as Daisy.
- Popular commercial cut flower in the world.
-Propagated by seed ,stem cutting and division.

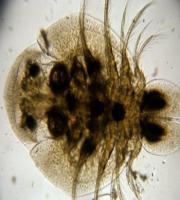
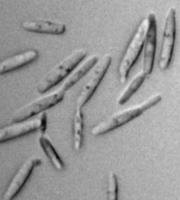
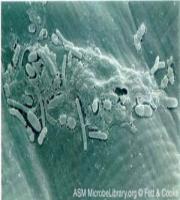
Disease caused by Crustacean.
This is commonly known as carp lice.
Secondary infection
As a result the carp become weak and even death may occur.
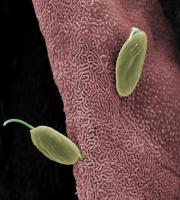
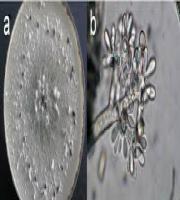
Protozoan disease
Pathogen: Ciliated, having prominent denticular ring
High bacterial loads provide abundant food for Trichodininds,

Protozoan disease.
Also known as White spot disease or Ich.
Most common in carps.
The parasites are often introduced through infected fish or pond equipment.
Changes in environmental conditions such as, the introduction of lower temperature water to that of the pond or tank can also cause the release.
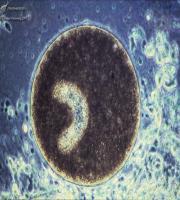
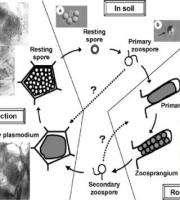
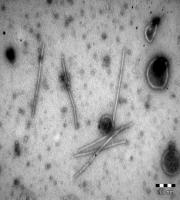
It is a protozoan disease.
Also known as Whirling Disease
The parasite does not infect humans or predators that eat infected fish; trout and salmon with whirling disease can be safely eaten.

The disease is spread by fungal cysts which are released in the faeces and by cannibalism of infected fish.
Particularly severely affected organs are:- liver, spleen, heart(herring), kidney, gonads,brain, gills and musculature and nerve tissue behind the eyes depending upon fish species
Diseased fish shows curious swinging movements hence the disease is called as swinging disease.
It is also known as “Reeling Disease”.
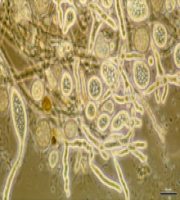
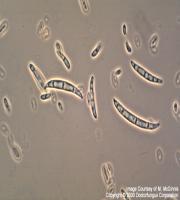
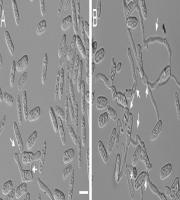
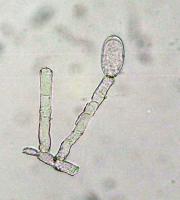
EUS is an infection caused by an oomycete fungi known as Aphanomyces invadans or A. piscicida.
Also known as :
An epizootic condition of wild and farmed freshwater and estuarine fish
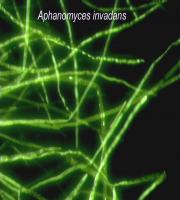
Also known as Gill Rot
Both species of fungi are found in fish suffering from an environmental stress, such as low pH (5.8 to 6.5), low dissolved oxygen, or a high algal bloom.
Branchiomyces sp. grow at temperatures between 57° and 95°F but grow best between 77° and 90°F.
The main sources of infection are the fungal spores carried in the water and detritus on pond bottoms.
Fish becomes weak and lethargic
Inflammation of liver and intestine.
Also known as Cotton Wool or Water Mould Disease
Most common fungus affecting fishes, especially major carps.
Mainly a secondary infection seen after damage to the fish integument.
Causes: Water pollution and overcrowding

It is also a contagious disease.
Medium and large size fishes are affected by this disease.

Leads to lethargy and loss of appetite
Caused due to bacterial infection.
Results in the putrefaction of Caudal fin(Tail) or other fins.
Fin and tail rot are associated with poor sanitary conditions in fish ponds and with water pollution in nature.
If the disease is left untreated, the disease can spread to other areas of the body.

Buildup of fluid inside the body cavity or tissues.
Can indicate a number of underlying diseases, including bacterial infections, parasitic infections, or liver dysfunction.
Most feared disease in carp culture.

An acute or chronic disease of fishes
Bacterial disease
Specially affected : IMC, Exotic carp,Gold fish and cat fishes as well
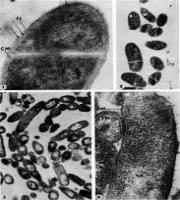


Both adult and larval stages feed on seeds within the pods.
Female deposits an egg at a site where she has been feeding. Small cavities and shallow furrows are typical forms of injury.

Leaves folded together with tender shoots showing bore . It has holes.
The larva leaves the shelter to feed, and lines the shelter with silk.

Developing pods show feeding punctures inside and grains become shriveled, they suck cell sap.

Lays eggs on leaf surface especially neat the petiole ends
Causes drooping of the tender leaves and seedling wilt.
The fly oviposits eggs into the tender pods.
The larvae then feeds on the epidermis and enters the seeds and damage them

Feed on the floral buds and flowers
Attacked flowers become brownish and unattractive
Larvae are beneficial.

When disturbed, larvae regurgitate a greenish, bitter-tasting, defensive chemical. the larvae pupate inside the leaf nest.
The pupal stage is the overwintering stage.


Damage symptoms include feeding punctures appearing as black or brown spots and presence of a large number of shiny, olive-green near circular bugs on the plants.
Larval and adult stages will feed upon the leaves, flowers and pods of the bean plant
The upper surface of the leaves dries out after the lower section is injured, giving a lace-like, skeletonized appearance.
Occasionally blossoms, and in many cases small pods, will be entirely destroyed.

Caterpillars eat away leaves and soft portions of stems and branches.
In severe, infestation the entire plant can be defoliate.

Pods become malformed .
Caterpillars feed on reproductive parts of the flower.
Later they web the inflorescence with leaves, pods and then feed within.
They damage seeds as well as cause flowers, buds and pods to drop.
It also enters into the pod and feeds on developing grains.

Adults and new born suck sap from litchi sitting at fruit stalk. Fruit drops occur once infected. Fruits of infected plant are not tastier.
They also infect the young branches.

Diseased pant. Poorly developed plant .
They transmit several diseases like mild mosaic. High density of aphids found in leaf surface.
Holes are found at the region of branching of stems. Web like structures fou
nd in the branch and stems. Abnormally developed
plant. Dried branches.
Surface of pomegranate contains black and brown colored holes.
Bark contains brown spots. Smell from the fruit. Early dropping of fruits.

The mites puncture and lacerate the tissues of the leaf and suck the cell sap.
- They attack the young leaves causing hairy blister like gall on the upper side of the leaves. The leaves also become thickened wrinkled and distorted and may ultimately fall off.
- The mite also attack and cause malformation of inflorescence.
Early symptoms of the infestation are the presence of small pinhead sized holes on the stem, fibrous extrusions from bases of leaf petiole and exudation of a gummy substance from the holes on the pseudostem.
- In advanced stages of infestation, the stem when split open will show extensive tunneling both in the leaf sheath and in the true stem. Rotting occurs and foul odour is emitted. Weakening of the stem by larval tunneling often result in breakage by wind.

The tent caterpillar feed on leaves and also modifies the leaf margin into web like structure (Tent).
- The caterpillar being voracious in nature feed heavily and defoliate the tree.

These insects suck the sap which result weak young plants in the nursery.
- The leaves, twigs, fruits and sometimes even the entire bark may be seen covered with ashy-grey scales.
- The affected fruits present pink colored areas around the scales and the market value of such fruits is reduced.

It causes the damages in Nursery bed. It destroys the soft part of stem, roots and leaves by sucking the vital sap from the tissue.
- In severe case of infestation, few warts can be observed and lead to low production of fruits.

The adults of pyslla suck the sap from young saplings. As well during sucking of sap, the insects also release the poisonous products in the leaves that cause the leaves distorted.
- The insect also deposit the honey like sweet product in leaves that make the favorable environment for the growth and development of Sooty mould.
- Citrus Psylla is the major vector insect for transferring Greening disease bacteria.

The caterpillars feed on the leaves and especially young seedlings and trees are seriously affected.
Complete defoliation occurs in severe attack.

Nymphs and adults damages the citrus plants by sucking the vital sap from the leaves, stems and fruits which stunted growth.
Soft scaled bodied insects produce honey like sweet products which provide favorable environment for the growth and development of Sooty mould and results in blackish appearance of leaves and stem.
Reduced Flowering

The female flies puncture the soft and tender fruits with their stout and hard ovipositor and lay eggs below the epidermis.
- On hatching, the maggots which are voracious in nature feed inside on the pulp of fruits.
- The infested fruits can be identified by the presence of brown resinous juice which oozes out of the punctures made by the flies for oviposition.
- These punctures also serve as an entry for various bacteria and fungi which results for rotting, distortion and malformation and pre-matured falling of fruits.

The grubs make tunnel in a zigzag manner through the pulp, endocarp and the seed coat.
- The grubs feed on the cotyledons and destroy them.
- The adults which emerge from the pupae feed on the developing seed and this may hasten the maturity of infested fruits and cause damage of fruits

- Both the nymphs and adults suck the sap from the inflorescence in large numbers causing withering and shedding of flower buds and flowers which result in poor fruit setting.
- The honey dew excreted by them affords conditions for development of sooty mould.

Nature And Damage of Maggot:
The maggots feed on seedlings, transplants and bulbs. Infested plants wilt and turn pale green to
yellow. First generation maggots in the spring cause the most damage. Young plants are more
susceptible to attack and can be killed, established plants are damaged but not usually killed.
Feeding damage causes misshapen bulbs and allows the entry other species of maggots and decay
organisms.
Control:
The onion maggot life cycle lasts from 37 to more than 60 days.The first-generation adults emerge
from pupae around mid-May in the northeastern US, with peak flights occurring about 2 weeks
later. Adults can survive for 2-4 weeks and may lay hundreds of eggs, beginning approximately 7
to 10 days after emergence.
Nature And Damage of FLY
It feeds on onion, garlic and chews both in the field and in stores. When plants are attacked, the
leaves start to turn yellow and the bulbs rot quickly, especially in damp conditions. Control
measures include crop rotation, the use of seed dressings, early sowing or planting, survey and
removal of infested plants, and autumn digging of the ground to destroy the pupae.
Control Measures
Application consist of placing sand soaked with a cupful of kerosene in a bucket of dry sand at the
base of the plants along the row is very effective for deteriing the parent files from depositing their
eggs. This will also kill young maggots that might attempts to work through sand.
Bulbs infested with bulb mites may rot and fail to produce new growth, or new growth may be off
color, stunted, and distorted.
Once the mites are inside the bulb, they rapidly turn the bulbs into rotten pulp.
Apparently bulb mites can attack healthy new roots and corms, especially in greenhouses. The
mites may penetrate into lily stems which become brittle. Infested lilies are often dwarfed,
distorted, and the stem roots are suppressed.
Bulb mites may enter prematurely opened tulip buds and cause bud necrosis.
Spider mites are two-spotted arachnids that change color from pale green to orange or red when
the weather becomes cold. They suck chlorophyll from the leaves, causing white translucent spots
and a silky web that can cover the whole crop.
CONTROL:
The garden pests can be controlled by natural predators such as beneficial mites, ladybugs,
lacewings, parasitic wasps, and spiders. They can also be eradicated by an organic spray which
needs to be applied on a weekly basis.

The most common vegetable bugs are the mealy, squash, and stink bugs. The three pests are well
known to pierce the stems and leaves and suck the sap, causing crop distortion and stunted growth.
They are pale pink, grey or white and popular in sheltered gardens.
CONTROL:
These bugs can be controlled by natural sprays such as garlic fire and predators such as wasps.
They can also be managed by methylated spirits, smothering oils, and physical methods such as
squeezing and crushing with hand
It is well known to cause great damage to beet, spinach, and chard.
CONTROL:
These harmful insects can be controlled by a suitable insecticide. They can also be controlled by
biological sprays, wasp predators which eat the larva and mechanical methods such as destroying
infested crops and eliminating weeds.

| Tiny holes , pinholes, chewed leaves by adult insect. Adult insects are 1/16" long, hard-shelled, shiny, dark-colored beetles that jump when disturbed. Slender, whitish, cylindrical larvae feed in or on roots but root damage is generally minimal. CONTROL: Dust with Rotenone. Keep debris removed. Rotate location of planting from year to year. |
|
Leaves wilt and growth is stunted. Insect is common, white, root feeding maggot. 1/4" long adult flies emerge from the soil about the time cherries bloom and lay eggs at base of plants in surrounding soil. Legless larvae feeds on host plant for three weeks, riddling the roots with brown tunnels before they pupate . Two or three generations can occur each growing season. |
| They feed on foliage, chewing out notches, damage is usually not severe. |
The maggots of the Carrot Rust Fly damage plants by eating the small fibrous roots and by tunneling in larger roots.
A rust-colored material develops in the tunnels, giving the insect its name.
Affected plants may become yellow, stunted, and die. Usually the plant tops continue to look healthy.
Maggots often continue to feed in stored carrots.
Disease organisms may enter the feeding tunnels and cause them to rot.
Neem has proven effective against this pest.
They are insect pests that can cause severe damage to sweet potatoes.
The larvae cause the most damage by feeding on the stems and storage roots.
When weevil populations are high, more than one preventive method should be used such as: use of clean planting material, planting early in
season and/or using early maturing varieties, selecting deep rooting varieties or earthing up the
soil around the base of the plant, removal of crop residues and volunteer plants, and crop rotation.
Majorly pests of yam in West Afica .
From egg to adult takes 22-24 weeks and emergence coincides with the beginning of the rains and the planting of yams.
Further attack occurs just before harvest when the beetles again feed voraciously and then migrate to the breeding sites.
The adult beetles burrow into the soil and feed on the tubers.
Preventive methods, such as planting as late in the season as possible and treating planting material with an insecticide before planting, are the best ways to control yam
beetles and reduce the infestation.
Both the adult and nymph suck sap from the collard/cabbage plant causing it to wilt, turn brown and die.
Younger plants are more susceptible to the feeding.
Larger plants can withstand higher populations but show reduced growth and yellowing.
Plants attacked by the cabbage maggot appear sickly, off color, and stunted.
If the attack is severe, they wilt suddenly during the heat of the day and die.
Cabbage roots show brownish grooves over their surface and slimy winding channels running through the flesh. Many of the small fibrous roots are eaten off.
Early cabbage after transplanting and late cabbage while still in the seedbed are most severely injured.

The larvae feed on all parts of the plant but prefer places around the bud of a young plant,crevices between loose leaves of a firm head, and the undersides of wrapper leaves.
Larvae will often not eat completely through the leaf, leaving tiny "windows" of thin foliage.
Their feeding may disfigure the bud of a young plant so that the marketable portion will not develop properly.
Cross-striped cabbageworms prefer the tender terminal buds and the heads of cole crop plants and riddle them with holes.
Eggs are laid in clusters, and large numbers of the larvae hatch on individual plants scattered over a field.
Cabbage webworms tunnel into and kill the buds of young plants.
Destruction of the original bud causes the production of secondary buds that cannot mature by harvest time.
Less severe injury may disfigure the head produced from the original bud.
Feeding on the outer leaves of older plants usually does little harm.
The shiny, light brown pupae are about one-fourth inch long.
They form in a web that is attached to fallen leaves and other debris on the soil surface.
Newly hatched larvae usually eat out small areas on the undersides of leaves.
As they grow, they move to the center of the plant, eating through the leaves between the veins.
Large larvae are heavy feeders and may cause serious damage to marketable heads especially when numerous.
Damage however, may at times be restricted to wrapper leaves.
The damage to the plant is caused mainly by the adult insects which feed voraciously on the leaves, flowers and fruits.
The beetle makes hole in the plant tissues, causing death or retardation of growth.
The damage done to young seedlings is often devastating.
The grubs of this pest remain in the soil and feeds on roots and stem of the plant.
At least three common cucurbit leaf beetles attack pumpkins in South Africa. They are all black and orange and damage flowers and leaves.
Its larvae feed on the roots of crops.
CONTROL :Cucurbit beetles must be controlled when they are first noticed in the spring.
Daily scouting is essential during the emergence and early life of the crop while the plants are small and suspect.

This pest stings young fruit (usually smaller than 10cm) and lays eggs in a cluster under the peel.
Infected fruit rots.
CONTROL: Put out bait consisting of Dipterex, sugar and water when flowering starts. Control with pesticide every seven to 10 day

Tomato leaf miner larvae feed on leaves and fruits, from seedlings to mature tomato plants.
Infestation is often followed by infections by secondary pathogens rendering infested crops unmarketable.
CONTROL: For an effective control strategy tomato growers should install and maintain pheromone traps formass trap monitoring of this pest in fields and greenhouses which are devoid of netting.
In case of such greenhouses, these should have installed pheromone traps or other mass trapping devices on the inside and should also have installed pheromone traps on the outside distributed throughout the perimeter.
High potato aphid populations can distort leaves and stems, stunt plants, and cause necrotic spots on leaves.
These aphids also secrete a large amount of honeydew that promotes development of sooty mold on foliage and fruit.
Plants are particularly susceptible to yield losses from high infestations during the period from 6 to 8 weeks before harvest.
Yield losses from equally high aphid populations decline substantially as harvest approaches, unless aphid densities are reducing leaf area enough to permit sunburn.

When the infestation is on shoots, they bend down and whither, affected leaves and shoot wither and dry.
At later stage of growth, caterpillars bore into flower buds and fruits , sometimes from under the calyx, when no visible symptoms are apparent.
Damaged flower buds are shed and fruits show circular holes. The large holes seen on fruits are usually the exit holes of the caterpillars.

Caterpillars roll leaves and feed on chlorophyll while remaining inside the folds.
The folded leaves wither and dry up.
Control : Collection and destruction of infested leaves along with insects in the initial stage help
to minimize the infestation.
Spraying of Carbaryl (0.1%) or Malathion (0.05%) controls the pest effectively.
Tomato fruit borer is one of the most destructive pests of tomato.
The adults lay majority of theeggs on the upper and lower leaf surfaces of the first four leaves in the top canopy.
The larvae scrape the tomato foliage until early or late second instar stage.
The larva bores into the fruit making it unfit for marketing.
In severe cases of infestation more than 80 per cent fruits get damaged.

The larvae sometimes roll the leaflets in large numbers and cause appreciable damage.

The mite attacks through basal plate of the bulb, or though the outer skin layers.
If a bulb is bruised or damaged in any way, mite development occurs more quickly. Roots may also be "mined" internally .
Cause damage by boring into onion bulbs and make cavities which lead to withering of plants.

The maggots bore into the bulbs, causing the plants to become flabby and yellowish.
It causes withering in the field and rotting in storage.
Damage leads to the invasion of Bacillus carolovorus which causes soft rot of onion.

Adults and nymphs lacerate the epidermis of the leaf and lap the exuding sap.
The affected leaves show silvery white blotches which later become brownis.
Bulbs remain undersized and get distorted, they transmit viruses.

White coloured scales are seen scattered on rhizomes and later they congregate near the growing buds.
Rhizomes are severely infested, they become shriveled and desiccated affecting its germination.
Early instars feed on the lamina of the freshly emerged leaves.
Later instars feed voraciously on leaves leaving only the mid ribs
Nymphs occurs on the under surface of the leaves and suck the sap.
Infested plant becomes stunted and covered with honey dew and sooty mould later.

The caterpillars damage terminal shoots by boring into them.
Drying of terminal portions of the vines.
The pest infestation is higher during July-November when numerous new shoots are available on the vines.

The thrips make marginal galls on leaves within which they live in colonies
Rasp and suck the sap
Leaf tissue become thick, crinkled and brittle.
Causes the leaf margins to curl down and inwards resulting in the formation of marginal leaf galls.

Larvae feeds into irregular holes .
On mature leaves, the beetle scrapes the green matter leaving the layer of upper epidermis.
The adults feed on tender shoots, spikes and berries.
The infested shoots and spikes turn black and drop.
The grub on emergence bore into the berries, feed on the internal contents and make them hollow.
The infested berries turn yellow initially and then black and crumble when pressed.
The pest population is more severe in shaded areas.
During the period from January to April the adults do not breed but remain in the field feeding on older leaves.
|
Grubs tunnel and feed on the rhizome causing death of entire clumps of cardamom. There is drying of the leaves and breaking up of the stem at the base. The pest becomes a serious menace in secondary nursery during November-January. |

Larvae feed on the growing shoot of the young cardamom suckers.
Emerging maggots feed the core tissue resulting in drying of the terminal leaf and cause dead heart symptoms.
Infestation is more on plants in open area; the pest activity starts during November and is at its peak in March-April.
The larva bores into the central core of the pseudostems resulting in the death of the central spindle causing “dead heart” symptom.
Larva feeds on seeds rendering them empty and prominent holes.
Early stage of the larva bores the unopened leaf buds and feeds on the leaf tissue.
They also bore the panicles leading to drying up of the portion from the affected spot
Feed on immature capsules and the young seeds inside rendering the capsules empty.
Late stage larvae bore the pseudostem and feed on the central core of the stem resulting in drying of the terminal leaf and thus produce characteristic ‘dead heart’ symptom.
Oozing out of frass material at the point of tunnelling is the indication for the presence of larva inside the plant parts.
The incidence of this pest is noticed throughout the year but they occur in enormous number in four periods, December-January, March-April, May-June and September-October and their abundance synchronizes with the panicle production, fruit formation and new tiller production.

Adults suck up plant sap and act as a vector of the mosaic or 'Katte' virus of cardamom.
Colonies of aphids are seen under concealed conditions inside leaf sheath.
These colonies are also seen in upper leaf sheaths and lower flower bracts of the ginger stem. The entire inflorescence may be infested. Small colonies occasionally occur on the leaf blade.
Ants are associated with the banana aphid. The ants feed on the honeydew secreted by the aphid and, in turn, establish new aphid colonies and ward off natural enemies.
Nymphs occurs on the under surface of the leaves and suck the sap.
Infested plant becomes stunted and covered with honey dew and sooty mould later interrupting photosynthesis of leaves.
Lacerates all aerial parts and feed on oozing sap.
Infestation on panicle and flower buds results in stunted growth of panicles, shedding of flower buds and warty growth.
The infested capsules are light in weight, inferior in quality, known as “cardamom itch”.
Grub causes the damage which made circular, pinhead sized bore holes.
The larvae are very active and move and bore into the commodity.
Females can lay 10- 100 eggs at a time, so can be very much severe quickly.

Nymphs and adults inject toxins resulting in whitening of veins and chlorotic patches.
Heavily attacked crop looks yellow and gives a scorched appearance known as 'hopper burn'.

The species is polyphagous nocturnal moth.
Larvae feed gregariously, scraping the chlorophyll, leaving only midrib in extreme cases.

Very common household pest, feeding principally on stored food products.
The larvae are surface feeders, they spin massive amounts of silk that accumulate fecal pellets, cast skins, and egg shells in food products.

Infestations arise from the presence of insects in the fabric of grain stores (including sacks), in grain being transferred from one establishment to another and in vehicles used for transportation.

This fly is highly polyphagous.
Larvae feed and develop on live and decaying plant material, feces, carrion and even the live larvae of other insects including the tobacco caterpillar.

Leaves become yellow, covered with black sooty mould.
Top leaves get dried up and lateral buds germinate.

Sacks are an important source of infestation.
Maize weevil will breed on maize in the field, but the Rice weevil only breeds in stored grain.

The cotton bollworm is a highly polyphagous species.
Larva feeds on silk and developing grains.

Nymphs and adults will feed on corn in any plant growth stage.
They start eating the leaves, silks (may interfere with pollination), and ear tips.

They feed on both sides of a leaf (upper and lower parts), including epidermis and the veins.
This feeding leaves gray to brown lines or "tracks" etched on the leaf surface.

The importance of a particular species of cutworm.
Some cause extensive crop damage, others are more like armyworms that climb the plant to feed on foliage.
Black cutworm is often considered as the most damaging cutworm species.
They cause holes chewed in leaves.
Leaf margins may appear ragged.
The caterpillars cause dead hearts in young plants.
The young plants can be pulled out easily.
The canes are damaged and rotten portion of the straw coloured shoot emits an offensive odour.
The central whorl of leaves dries up.

Corn leaf aphid acts as a vector of Maize dwarf mosaic virus (MDMV).
It causes leaf mottling and discoloration; reddening of corn leaves exacerbated under drought stress.
The aphid also produce a sticky honeydew. Opportunistic sooty mold fungi follow thereafter.

Female click beetles deposit their eggs in the soil of grassy or cultivated areas, reduce germination rate by feeding on germinating seed , damaging or eliminating a potential plant.
Wireworms may also injure corn by feeding on soft stem and root tissues underground.

White grubs live underground and feed on plant roots.
While larval damage is typically associated with feeding on corn roots.
Feeding may cause stunting, nutritional deficiencies and stand loss.

Leads to dead heart.
Larvae bore holes visible on the stem near the nodes.
They cause causing typical “shot hole” symptom.

It affects the maize plants at the seedling stage and leads to drying of the seedlings or ‘dead heart’.

Life cycle
The adult remain most active from 10-32°C. The females start laying eggs within 3-10 days of their emergence and deposit eggs in masses by lacerating the parenchymal tissue. The number of egg per mass varies from 2-11 and female lays on an average 124 egg masses. The eggs are somewhat dark and cylindrical having two distinct spots. The incubation period ranges between 4 to 8 days. The nymphs on emergence start feeding on young leaves and after moulting 5 times, they become adults in 2-3 weeks. The life cycle is completed in 18-24 days during June- October, 38-44 days during February to April.
Damage
Both nymph and adults cause damage by sucking the cell sap from the leaves which turn yellow. If insects attacks during early stage of growth, the entire plant may dry up. A heavy infestation produce the symptoms of Hopper Burn i.e leaves become dry and brown after insect feeding and patches of the burned plants are often lodged. It has been noticed that even at the low infestation the tillering is adversely affected and there diminished vigor and decreases in plant height. Under the favorable condition of high humidity, optimum temperature, high nitrogen application and no wind, the population increases rapidly and hopper burn is observed The insect is known to transmit the grassy stunt, ragged stunt and wilted stunt virus disease of rice.
Management

They are abundant during the rainy season.
The adult moths hide at the base of the plants in rice fields or in grassy areas during daytime and are active at night.
They cause scraped leaves.

The larva feeds on the foliage by scrapping chlorophyll leaving horizontal rows of green material.
The leaf tips are sharply cut off and the cut portions are turned into cylindrical tubes.

Rice skipper feeding damage causes removal of leaf tissues.
They roll leaves and make a protected chamber.
They also use silken threads to roll up and stitch together partially eaten leaves.

They stay between the leaf sheath and stem to feed and complete their entire larval development.
They cause white waxy fluff in leaf sheaths.

Staggered planting and heavy nitrogen supply encourages population growth.
They spread the viral disease tungro.
They lead to yellowing disease and reduced number of productive tillers.

Instars bore into the leaf sheath and causing longitudinal yellowish-white patches.
Severe feeding causes deadhearts at the vegetative stages and whiteheads at the reproductive stages.

Irritate the tissues of the rice plant forming tubular gall at the base of tillers, causing onion leaf or silver shoot.
This is a pale cylindrical, hollow tube with a green tip replacing the normal culm.

Scrapes the upper surface of leaf blades leaving only the lower epidermis.
It also tunnels through the leaf tissues.
Causes withering of damaged, whitish and membranous leaves.
The eggs are found on the tip of leaf blades.
Both the adult and the larvae destroy the crops.
Effects every life stage of crops, especially effects the vegetative stage of the crop , generally in water stagnant field.

They bind together leaf margins with silken strands,
Then, feed creating longitudinal white and transparent streaks.

Adult and nymph root aphids suck the plant to remove the fluids.
The feeding damage causes the yellowing of leaves and stunting.
Rice root aphids are dominant in well drained soils in upland and rainfed rice.
They are not present in irrigated rice.

Adults suck the milk from the developing grains and stem,
Discoloration and presence of some empty or ill filled grains.
Infested paddy straw contains foul smell

Feed on immature cotton balls and on the developing and ripening seed.
Cottony yellowish below the part which bug sucks

Causes naked (skeletonize), cut crops .
Maximum infestation at rise of spring.
Also damage inflorescence, ears, grains

Causes drying of plants with damaged underground stem and easily pulled by hand.
Controlled by red ants
Damage in rice are dead heart in young plants and white ear.
In sorghum and maize, dead heart symptom with central shoot drying up, red mining in the midribs, windows in the leaves , shot holes on the whorl leaves and boreholes at the base of stem

Hollow main primary root beneath the soil filled with soil,
tunnels found along the shoot filled with soil,
Causes wilting

Infestation usually occurs during second fortnight of January till crop maturity.
Cause yellowing of leaves (because of excessive sap removal), dwarfing , with red spots.
"Honeydew " is the large amount of sugary liquid wastes produced by aphids.
Fungus called sooty mold grow on honeydew turning leaves and branches black (this may be the first time aphid infestation noticed)
Lady beetles and lacewings are natural enemies of aphids.
|
· Destroy infected tubers. · Controlled irrigation combined with Sulphur treatment. |

|
· Use healthy plant seeds. · Spray 5-6 times Carbendazim(0.1%) or mancozeb fortnightly. |
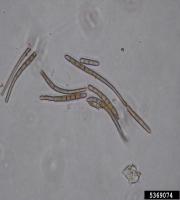
|
· Azotobacte spp as bio-control agents. · Seed treatment with Thiram. · Spray blitox50, Mancozeb(0.25%) at 10-15 days interval. RV:
|
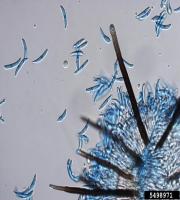
|
· Intercrop with marigold. · Deep summer ploughing resistance varieties:
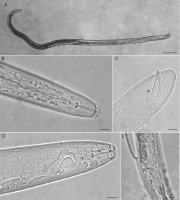
. · |
|
· Only preventive. · Control of vector(Bemesia tabaci) is a most effective measure. |
|
· Only prevention · Sanitation |
|
· Only prevention · Sanitation |
|
· Sprinkle irrigation to avoid foliar infection · Sorting out diseased parts · Foliar apraying of Metaxyl + Mancozeb Resistamce varieties:
|
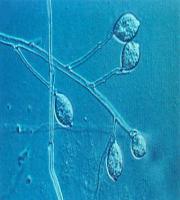
|
· Proper irrigation · Ventilation · Limestone application |
*Treatment of seed with bavistim @2-3 gm/kg seeds..
*Mixing Menkozeb 75% wp (Dithene M-45)3gm/litre or propineb 70%wp(Antracol,KiAntra,Antragold)3gm/litre of water and spraying at 15 days interval for 3 time.

*use balanced amount of plant nutrient ,especially nitrogen.
*Use resistance varieties like( radha 4,7,11,12,,swarna 2,9,,sukkha 1,2)
*Treatment of seed with agromycine -100@0.25gm/litre of water for 30 min.
Management
Caused by cochliobolus heterstrophus
Management: crop rotation, Tillage and fungicide application

Seedborne fungal disease..
Use clean seeds.
Apply fungicide containing benomyl.Avoid repeated application of benomyl since the fungus can develop resistance to treatment
It is caused by Exserohilum turcicum. Infection occurs when free water is present in the leaf surface for 6 to 18 hours and temperature of 65 to 80F.
Resistance variety:manakamana -1
Management-crop rotation, tillage and fungicides applications
*Leaf smut ,caused by fungus Entyloma oryzae is a widely distributed ,but somewhat minor,disease of rice.
*The fungus produces slightly raised,angular ,black spots(sori)on both sides of leaves.
*The fungus is spread by airborne spores and over - winters on diseased leaf debris in soil.leaf smut occurs late in the growing season and causes little loss.The disease is favoured by high nitrogen rates.
|
· Spray benomyl 50% wp @ 0.5ml/litre drenching the soil · Maintain the pH level of soil above 7.2 · Flusulphmide 0.3% wp 10-15 kg per ropani or 3 gram per plant, 3 kg per 10 m2 in nursery bed |
|
· Affected plants are burnt · Aphids are destroyed · Red varieties of Mustard are more resistant
|
|
· Seed treatment with 50% wp carbendazim · Avoid crowding in nursery plants · Mancozeb 75% wp spray @ 3gm/litre
|
|
· Crop rotation with crops of other family · Eradication of diseased plants from field
|
· Diseased stems are burnt
· Water is kept standing for 3 weeks to 1 month before planting crops in affected field
· Crop rotation with rice
Deep ploughing
· Affected plant parts are collected and burnt
· Mancozeb 75% wp @ 3gm/kg seed
· Mancozeb 75% wp / spray copper oxychloride 50% wp 3gm/litre

|
Use of certified seeds. Early sowing of seeds Mineral oil followed by pyrethroid. |
Resistance varieties.
Use of certified seeds.
Intercropping with maize.
Aphid control by metasystox.
Early planting to insect high insect populations
|
Deep plough, balanced potash and zinc application. B. subtilis Biocare-F |
Bavistin 0.1%
|
Avoid sprinkler irrigation. Seed treatment captan 50% WP |
Blitox 50% or mancozeb 75% WP 3gm/litre spray
|
Destruction of diseased plants debris after harvest. In seedlings 2:1 lime:neem dust |
Sulphur 80% WP, Mancozeb (0.2%)

|
Burn plant debris and clean cultivation. 2:1 mixture lime and neem dust spray. Sulphur dust 25kg/ha or karathene 2% |
Carbendazim 50% WP
|
Resistance varities |
|
Rachana PM-2 |
Parts used: Bark,carpels, carpels of fruits, seeds
Medicinal use: Carminative, stomachache, anti rheumatic, tonic, hepatitis.
Parts used: Rhizome
Medicinal use: Inhibit cancer cell growth, anti itching, antipyretics, useful as antidote, laxative
Parts used: Rhizome
Medicinal uses: Used as tonic, powder of rhizome are administered during pre and post pregnancy period.
Parts used: Leaves, twigs, flowering apices.
Medicinal uses: For muscle pain, improve memory, to boost immune, circulatory system, promote hair growth.
Parts used: whole plant
Medicinal uses: Tonic aphrodisiac, cardiactonics, expectorant, hypertension,acute and chronic hepatitis.
parts used: Stem, leaves
Medicinal uses: Fix stomach spasms, loss of appetite, intestinal gas, kidney condition, head cold, warts. Also has aromatic uses.
Parts used: Fruit, seeds, bark
Medicinal use: Bark used as astringent, treatment of ulcers, laxative.
Parts used: Tuber, fruit
Uses: used in hemoptysis, epitaxis, pharyngitis, goitre, sprains and injuries.
Parts used: Seed, leaves
Uses: Buddha chitta is used to make people happy to protect people from suffering and diseases.
Parts used: rhizome
Uses: Flavoring agent
parts used: Leaves and fruits
uses: Aromatic leaves and carminative
parts used: bark and fruits
Uses: Aromatic and carminative
parts used:Seeds
Uses: Seeds as aromatic agent and stimulant
Parts used: Leaves, tender shoots, fruits
Uses: Used as a flavoring agent in foods, curries and salads
parts used: frozen, dry or fresh leaves
uses: flavor similar to anise and used for bringing soothing smell to culinary purposes.
parts used: dry and fresh leaves, seeds and stems
uses: flavor similar to fennel used in culinary purpose for brining distinct aroma
parts used: ground seeds and fresh leaves
uses: aroma in culinary purposes, waxy and somewhat orange complex
parts used: immature flower
uses: intense aroma and flavor in foods
parts used: bulbs and shoots
Uses: sharp flavor in culinary purposes
parts used: stigmata
uses: aroma strong and sweet flavor, colouring yellow
parts used: fruits and fresh leaves
Uses: for aromatic and sweet flavor
Parts used: fresh or dry bulb and dehydrated shoots
Uses: For sharp flavor and intense aroma
Used for treating gastritis.
Parts used:Whole plant, fruit and seeds
medicinal use: diuretic, inflammatory, appetiser, stomachic
parts used: bark and oil
medicinal uses: bronchitis, asthma, cardiac, disorder, fever
parts used: Rhizome and leaves
medicinal use: sedative, analgesic, epilepsy and hypersensitivity
parts used: seeds, bark
medicinal uses: Cough, insomnia, dropsy, vomiting, ulcer and used as Trifala
parts used: Seeds
medicinal (other) uses: (Trifala) wound ulcer, leprosy, inflammation and cough.
parts used: Whole plant
medicinal use: Leukemia, hypotensive, antipasmodic and antidote.
parts used: Leaves
Medicinal use: Laxative, wound healing, skinburns and skincare, Ulcer
parts used:leaves, flowers and oil extract
medicinal use: digestive, pain killer
Parts used: Root, fruit and leaves
Medicinal Use: Skin disease, Snake bite and helminthiasis
parts used: Leaves and seeds
Medicinal use: cough, cold, bronchitis and expectorand
parts used: dry tubers
medicinal use: Rheumatism, general debility, tonic and aphrodisiac
Parts used: tuber, root
medicinal use: enhance lactation, general weakness, fatigue and cough
parts used: root
medicinal use: hypertension and insomnia
parts used: heartwood oil
medicinal use: Skin disorder, burning senastion, jaundice and cough
parts used: root
medicinal use: kidney stone and calculus
parts used: fruit/ whole plant
medicinal use: dropsy, general debility, diuretic and anti dysenteric
parts used: fruit, root
medicinal use: appetiser, enlarged spleen, bronchitis, cold and antidote
parts used: whole plant
medicinal use: fever, weaknes, release of gas
parts used: Seed, tuber
medicinal use: skin disease, labour pain, abortion and general debility
parts used: Stem
Medicinal use: Gout, piles, general debility, fever and jaundice
parts used: gum, resin
medicinal use: rheumatic disease, arthritis, paralysis and a laxative
parts used: Leaves
medicinal uses: diabetes, hydrocoel and asthma
Parts used: whole plant
medicinal use: nervous, memory enhancer and mental disorder treatment
parts used: Whole plant
medicinal use:skin disease, burning sensation and fever
Parts used: Whole plant
Medicinal use: Anaemic, jaundice and dropsy
parts used: fruit and bark
medicinal uses: diarrhoea, dysentery and constipation
parts used: roots and leaves
medicinal use: restorative tonic, stress, nerves disorder and aphrodisiac
parts used: bark, flower
medicinal use: menstrual pain, uterine disorder and diabetes
Parts Used: Fruit
Medicinal use: Vitamin - C, Cough , Diabetes, cold, Laxative, hyper acidity.
Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP
Growth habit: erect and strongly tillering; up to 0.75 m
Moisture: wet Competitiveness: low to moderate
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: wet or dry cultivation; early flooding;dry field to stop regrowth after rice harvest
Reported resistance: ALS inhibitors (JAP, KOR)
Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.2 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Dormancy: 2 to 3 mo Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS > TP
Growth habit: erect and strongly tillering; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: moist to wet Emergence time: within 7 d
Competitiveness: moderate; strong root competition
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: early flooding; hand weeding
Reported resistance: ALS inhibitors (BRA); synthetic auxins (MAL)
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.02 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Flowering time: 30 d Dormancy: none; light requirement for germination
Elevation: up to 1,000 m Light: sunny

Found in: upland, lowland Establishment method: DS, WS
Growth habit: erect; variable in habit and infl orescence
size, up to 0.7 m Moisture: dry to wet
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: early flooding; hand weeding, tillage
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.1
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, rhizomes
Dormancy: unknown Elevation: up to 2,500 m Light: sunny

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: erect; tubers in chains on rhizomes; up
to 0.7 m Emergence time: simultaneous with rice
Moisture: dry to moist Competitiveness: moderate to low, but competitive early Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: stale seedbed; suppressive crop with narrow rows; high plant density; fl ooding suppresses
growth but does not kill tubers; interrow cultivation
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.1
Method(s) of reproduction: tubers, rhizomes
Maturity time: from 21 to 56 d Dormancy: yes, apical dominance in tubers
Elevation: up to 1,800 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS, WS >> TP
Growth habit: erect; tufted up to 0.8 m
Emergence time: within 7 d Moisture: moist to wet
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: early flooding; hand weeding
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.1
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Maturity time: as little as 30 d
Dormancy: yes; can germinate about 75 d after shedding
Elevation: up to 1,200 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS > TP > DS
Growth habit: tufted and erect; up to 1.0 m
Moisture: wet to moist Emergence time: within 7 d; continual throughout season Competitiveness: moderate
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: early continuous fl ooding, hand weeding,tillage Reported resistance: ALS inhibitors (AUS, BRA, ITA,
KOR, ESP, USA) Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.01
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Maturity time: as little as 30 d
Dormancy: none Elevation: up to 1,400 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS, TP > DS
Growth habit: erect and slender stem arising from tuberous
base; up to 1.5 m Moisture: wet to flooded
Emergence time: within 7 d of last tillage
Competitiveness: high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: rotation; deep tillage may bury tubers;
alternately, long drainage periods and zero tillage
Reported resistance: ALS inhibitor (KOR)
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 5.6
Method(s) of reproduction: tubers > stolons > seeds
Dormancy: yes, in tubers Elevation: up to 3,000 m
Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: tufted, erect, and branching; rooting at
nodes; up to 3 m Moisture: dry to moist; well-drained
Competitiveness: very high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: clean seed and implements; fl ooding;
rotate to broadleaf crops; control in nearby areas
Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitors (USA)
Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 15 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Dormancy: 1 to 4 mo; after-ripening requirement
Elevation: up to 1,500 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: erect, tufted, and rooting at lower nodes; up to 1 m
Moisture: flooded to moist Competitiveness: low
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: tillage; deep fl ooding; hand weeding Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, rooted stem fragments
Maturity time: 90 d Dormancy: undetected
Elevation: up to 3,000 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS, TP
Growth habit: creeping branched stolons, erect stems; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: moist to wet Competitiveness: high
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: thorough land preparation; early continuous flooding; tillage during dry season to desiccate
rhizomes Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial
Method(s) of reproduction: stolons > seeds and rhizomes
Maturity time: 82 d Dormancy: yes, perhaps requires cold to germinate; apical and bud dominance in new stems
Elevation: up to 1,500 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: creeping; erect and branching stems; up
to 1.0 m Moisture: dry to moist; drought-tolerant
Competitiveness: perhaps moderate
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: flooding; tillage or cutting
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.67
Method(s) of reproduction: rhizomes, seeds
Maturity time: rhizomes in 30 d; flowers in 50 to 60 d
Dormancy: unknown Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny; shade-tolerant

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS, DS
Moisture: moist to flooded
Emergence time: with sown crop or soon after
Competitiveness: high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: stale seedbed, early fl ooding, hand
weeding, water seeding, transplanting rice Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 20-30 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Elevation: as for rice crop Light: as for rice crop

Found in: lowland Establishment method: DS > WS > TP
Growth habit: tufted, erect, and slender; sometimes with reclining stems; up to 1.2 m Moisture: aquatic—wet to fl ooded
Competitiveness: high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: thorough land preparation and hand
weeding; permanent fl ood within 1 week
Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitor (THA)
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.1 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, plant fragments Dormancy: low or none Elevation: up to 1,400 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS, TP > DS
Growth habit: creeping to ascending, tufted, and erect; up to 1.2 m
Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet Competitiveness: moderate to high
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: stale seedbed; rotavating/puddling in wet or dry conditions
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.8
Method(s) of reproduction: rhizomes, seeds
Dormancy: unknown Elevation: up to 2,200 m Light: partial shade to sunny

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS >> WS, TP
Growth habit: tufted, ascending to erect, and muchbranched; up to 1.0 m
Emergence time: within 7 d Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet
Competitiveness: high Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: early continuous fl ooding; early removal
Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitor (COL), bipyridiliums(MAL)
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 4 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, rhizomes
Maturity time: 130 d Dormancy: yes; light required for germination
Elevation: up to 2,400 m Light: sunny; shade-tolerant

Found in: upland
Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: erect, tufted, and unbranched; scaly rhizomes;up to 2 m
Moisture: moist to dry; well-drained
Competitiveness: high
Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: legume cover crops; repeated tillage to desiccate rhizomes; flooding; rotation
Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial
Seed wt: 1
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, rhizomes
Dormancy: none in seeds, but lateral buds are dormant; seeds viable for up to 1 year
Elevation: up to 3,000 m
Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: stems erect or ascending, branched; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: moist to wet Competitiveness: high
Seed contaminant: unknown Cultural control: early continuous flooding; hand weeding Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitor (BOL, BRA, MAL),
ALS inhibitor (COS), bipyridiliums (MAL, USA), dinitroanilines (USA), multiple: ACCase inhibitor + glycines (MAL) Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.4
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Maturity time: fl owering in 30 d; maturity in 4 to 6 mo Dormancy: some, but usually short
Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive
Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS > TP
Growth habit: erect, tufting up to 2 m Moisture: wet to moist
Competitiveness: very high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: thorough land preparation; early, deep
flooding; rotation Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitors (CHN, THA, USA),
chloroacetamides (CHN, PHI, THA), dinitroanilines (BUL), photosystem II inhibitors (CAN, CZE, FRA, POL, ESP, USA), synthetic auxins (BRA, USA), thiocarbamates (CHN, USA),ureas and amides (GRC, PHI, THA, USA), multiple resistance(BRA, PHI, THA, USA)
Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 3 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Flowering time: 42 to 63 d Dormancy: variable, up to 4 mo
Elevation: up to 2,500 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: tufted and erect; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: dry to wet Competitiveness: high
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: early cultivation; early flooding; hand weeding Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitors (BOL, COS, NIC),
ALS inhibitors (BOL, COS), glycines (AUS), photosystem II inhibitors (AUS, IRN), ureas and amides (COL, COS, GTM, HND, PAN, SLV, VEN), multiple resistance (COS) Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 1.0
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, stolons Flowering time: 30 to 45 d
Dormancy: low or none; light requirement for germination
Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny, partial shade

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS Growth habit: creeping, tufted with prostrate to erect culms; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: dry to moist Competitiveness: moderate to high
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: flooding, early removal by hand
Reported resistance: ACCase inhibitors (BRA) Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.6
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Dormancy: variable, up to 7 mo
Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: upland, lowland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: creeping with ascending culms; up to 0.6 m
Moisture: moist Emergence time: shortly after rainfall
Competitiveness: moderate to high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: stale seedbed; flooding; early removal by hand
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.3
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Maturity time: 28 d; senescence in 4 mo
Dormancy: unknown Elevation: up to 1,000 m Light: sunny, partial shade

Found in: upland, lowland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: prostrate to ascending; up to 0.4 m
Moisture: dry to moist, drained Emergence time: 14 d
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: stale seedbed; tillage and removal; dry tillage to desiccate rhizomes; soil solarization
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.3
Method(s) of reproduction: rhizomes and stolons, seeds
Maturity time: tillers at 25 to 30 d; maturity at 120 d Dormancy: no; seeds survive 50 d of submergence
Flower: white or pinkish, very small Elevation: up to 2,300 m Light: sunny, partial shade

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: prostrate to ascending, much branched,
with fleshy leaves; up to 0.5 m
Moisture: dry to moist Emergence time: with rice
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: flooding; tillage often ineffective because
of stem regrowth; do not allow to mature; remove
fruiting plants from fi eld to stop shedding
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 1.3
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Maturity time: flowers in 20–30 d; maturity about 20 d
after pollination Dormancy: secondary; long viability because of hard seed
Flower: white to pale pink Elevation: up to 800 m Light: partial shade

Found in: lowland Establishment method: DS, WS > TP
Growth habit: erect, branched herb with hollow stems;
up to 1.5 m Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet; prefers stagnant water
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: closed crop canopy limits weed growth
Reported resistance: synthetic auxins (PHI, MAL, THA)
Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.01
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Dormancy: yes; light requirement for germination
Flower: small and white Elevation: up to 300 m Light: partial shade to sunny

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS >> WS
Growth habit: succulent branched spreading herb; up
to 0.5 m Moisture: dry to moist Competitiveness: low to moderate Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: flooding; repeated shallow cultivation
though re-roots readily Reported resistance: multiple to photosystem II inhibitor
+ ureas/amides (USA) Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.07
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds > stem fragments
Maturity time: flowers in 1 mo, maturity in 2 to 4 mo
Dormancy: low or none Flower: yellow
Elevation: up to 2,700 m Light: sunny to partly shaded

Found in: lowland Establishment method: DS, WS, TP
Growth habit: herb; erect or ascending; branched; up
to 0.6 m Moisture: flooded to damp; may require saturation for
establishment Competitiveness: probably low
Seed contaminant: unknown Cultural control: completely uproot by hand or tillage as
cut stems may resprout; control before fl owering
Reported resistance: photosystem II inhibitor (FRA)
Life cycle: annual Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, sometimes rooted
stems Maturity time: flowering by 90 d
Dormancy: variable, but usually an after-ripening period;
light requirement for germination Flower: greenish yellow, pinkish Light: partial shade

Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP > WS
Growth habit: floating stoloniferous herb, sometimes
rooting; about 0.1 m Moisture: aquatic—flooded to moist
Competitiveness: probably low Seed contaminant: unlikely
Cultural control: drainage; physical removal Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Method(s) of reproduction: plantlets and seeds
Maturity time: stolons by 5- to 6-leaf stage; maturity at 120 d
Dormancy: yes, seems to require long submergence period
Elevation: up to 1,000 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP > WS
Growth habit: herb; erect, hairless and fl eshy; up to 0.5 m
Moisture: aquatic—wet to flooded Competitiveness: moderate with great densities early
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: stale seedbed with wet tillage, hand
weeding Reported resistance: ALS inhibitors (KOR)
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.07 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, perhaps stolons
Flowering time: within 60 d Dormancy: may need long anaerobic period to germinate
Flower: pale to dark blue Elevation: up to 1,550 m Light: sunny

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: prostrate to erect, many-branched shrub;
up to 2 m Moisture: dry to wet
Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: cutting or burning or hand weeding of
seedlings; probably early flooding
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 6
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Dormancy: yes, long; also long viability because of hard
seeds; broken by heat Flower: reddish purple to white
Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny to partly shaded

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS, TP
Growth habit: fern; creeping hairy rhizomes, erect or
leaves floating Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet
Emergence time: first 10 days after transplanting
Competitiveness: moderate, but can be severe early;
strong competitor for nutrients Seed contaminant: unlikely
Cultural control: minimize wet tillage; dry tillage after
harvest to desiccate rhizomes Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Method(s) of reproduction: spores, rhizomes, and fragments
of rhizomes Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: WS, TP
Growth habit: erect, much-branched and robust herb;
up to 1.5 m Moisture: wet to damp; drier than L. adscendens
Competitiveness: high Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: early flooding or hand weeding
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds and plant fragments
Dormancy: low or none; light requirement for germination
Flower: yellow, 4 petals each about 10 mm long
Elevation: up to 1,500 m Light: partial shade to sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP > WS
Growth habit: herb; floating or rooted and creeping; up
to 0.5 m Moisture: aquatic—flooded or wet
Competitiveness: low Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: hand weeding Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, plant fragments,
stolons Dormancy: unknown
Flower: white to yellow Elevation: up to 1,600 m
Light: partial shade to sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP > WS
Growth habit: vine, widely spreading and much-branched
Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet Competitiveness: low; greater early
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: physical removal though readily re-roots
from nodes Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 36 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, runners
Flowering time: 45–60 d Dormancy: yes; may require seed coat to be broken
Flower: white to cream or purple Elevation: up to 1,200 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland Establishment method: TP > WS
Growth habit: floating, rooted in shallow water; up to
0.3 m Moisture: aquatic—flooded to wet
Competitiveness: low to moderate; greater early, and
greater than many other aquatics Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: drainage and physical removal possible
with small infestations Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.1
Method(s) of reproduction: stolons, plant fragments,
plantlets developing from seeds Dormancy: variable—none to many years
Flower: blue to violet Elevation: up to 1,600 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: herb; prostrate to erect, much-branched;
up to 1.0 m Moisture: wet to moist
Competitiveness: low to moderate Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: cultivation and hand weeding; early
removal or cutting; high fertility Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.4 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Maturity time: 42 d Dormancy: none; light required for germination
Flower: white or cream Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: creeping or ascending; up to 1 m
Moisture: wet, not flooded Competitiveness: at least moderate
Seed contaminant: yes Cultural control: early continuous fl ooding; hand and
mechanical weeding diffi cult because pieces may re-root
Reported resistance: synthetic auxins (USA) Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 11.5
Method(s) of reproduction: stolons and by seeds Flowering time: earlier than rice
Dormancy: innate and induced by high temperatures Flower: blue
Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: shaded

Found in: upland, lowland Establishment method: DS >> WS
Growth habit: herb; up to 1 m; prostrate or ascending
Moisture: moist to wet; drier than C. diffusa Emergence time: 10 to 12 d
Seed contaminant: unknown Competitiveness: moderate
Cultural control: flooding; hand and mechanical weeding
may as stem pieces re-root Reported resistance: none
Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 2.0 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, stolons
Maturity time: aerial flowers in 35 d; rhizomes with underground flowers in 42 d
Dormancy: yes, innate Flower: purple or blue; those from underground stems
are whitish Elevation: up to 2,000 m Light: sunny to slightly shaded

Found in: upland Establishment method: DS
Growth habit: erect, much-branched; sharp axillary spines;up to 1 m
Moisture: moist Competitiveness: moderate to high Seed contaminant: unknown
Cultural control: early hand weeding (before thorns grow) or cultivation; flooding suppresses growth
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.2
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Dormancy: variable, none to 4 mo; long viability; no light requirement for germination
Flower: pale green-purple tinge Elevation: up to 1,800 m Light: sunny; shade-sensitive

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS
Growth habit: prostrate, creeping or ascending; many suberect branches, up to 1 m
Moisture: wet to moist; more terrestrial than aquatic Competitiveness: moderate
Seed contaminant: unknown Cultural control: flooding, hand weeding or tillage
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 0.5
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds, stolons, stem fragment Dormancy: unknown
Flower: white or pinkish, very small Elevation: up to 2,650 m Light: sunny

Found in: lowland, upland Establishment method: DS > WS Growth habit: erect, branched; up to 1.2 m
Moisture: wet to moist Competitiveness: moderate Seed contaminant: yes
Cultural control: high fertility; early removal by hand weeding or cultivation
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: perennial Seed wt: 7.3
Method(s) of reproduction: seeds Dormancy: yes, pronounced
Flower: yellow, often suffused with purple Elevation: up to 1,000 m Light: sunny

Found in: upland Growth habit: erect, often decumbent herb; up to 1.2 m Moisture: moist to dry Competitiveness: moderate
Seed contaminant: unknown Cultural control: early cutting or hand weeding and shallow cultivation
Reported resistance: none Life cycle: annual Seed wt: 0.1 Method(s) of reproduction: seeds
Maturity time: quick flowering and short-lived, as little as 2 months
Dormancy: 50% of seeds can germinate immediately; light required for germination
Flower: white to pale purple/blue Elevation: up to 3,000 m Light: shade-tolerant
